This is the multi-page printable view of this section.
Click here to print.
Return to the regular view of this page.
How to Guides
Welcome to our comprehensive How-To Guide for using kosi. Whether youre a beginner aiming to understand the basics or an experienced user looking to fine-tune your skills, this guide is designed to provide you with detailed step-by-step instructions on how to navigate and utilize all the features of kosi effectively.
In the following sections, you will find everything from initial setup and configuration, to advanced tips and tricks that will help you get the most out of the software. Our aim is to assist you in becoming proficient with kosi, enhancing both your productivity and your user experience.
Lets get started on your journey to mastering kosi!
1 - How to install KOSI as a user
Setting up KOSI on RHEL systems requires a few key steps, including downloading the RPM file and configuring your environment. Here’s a quick guide to help you through the process.
How to install KOSI as a user
This guide shows you how to install KOSI as a user. KOSI can be downloaded only from our official website.
Prerequisites
-
Operating System: A machine running RHEL 8.
-
Helm: Must be installed on your machine. Refer to the Helm Official Documentation.
-
Podman:
KOSI requires Podman to be installed on your machine.
Note: If you are a non-root user, ensure that the number of user namespaces (max_user_namespaces) is properly configured. For more details, refer to this GitHub tutorial.
Installation on RHEL8:
Important: Only supports secure registries. If you use an insecure registry, it is important to list your registry as an insecure registry in registry.conf (/etc/containers/registries.conf).
Installation Steps
-
Download the KOSI RPM:
- Log in to your KubeOps account.
- Download your desired version of the KOSI RPM from the official download page.
-
Install the KOSI RPM on your admin node:
Run the following commands:
echo 'export KUBEOPSROOT=/home/<user>/kubeops' >> $HOME/.bashrc
source $HOME/.bashrc
sudo dnf install <path_to_rpm>/<kosi_file_name>.rpm
Note:
- Replace
<path_to_rpm> with the directory path where the file is located.
- Replace
<kosi_file_name> with the exact RPM file name (including the .rpm extension).
$KUBEOPSROOT Variable
The $KUBEOPSROOT environment variable stores the location of the KOSI plugins, deployment.yaml, and config.yaml.
If you change the KUBEOPSROOT variable after installation, you must manually copy the updated deployment.yaml, config.yaml, and plugins.
Run the following commands to update:
echo 'export KUBEOPSROOT=/home/<user>/kubeops' >> $HOME/.bashrc
source $HOME/.bashrc
cp -r /var/kubeops/kosi/config.yaml $KUBEOPSROOT/kosi/config.yaml
cp -r /var/kubeops/kosi/deployment.yaml $KUBEOPSROOT/kosi/deployment.yaml
cp -r /var/kubeops/plugins $KUBEOPSROOT/
Note: For a clean installation, it is not necessary to move the deployment.yaml.
Check Installation
To verify that KOSI is installed correctly on your machine, simply run:
A successful installation will display version details, it will look like this:
2024-08-07 13:49:00 Info: KOSI version: 2.11.0.11_Beta0_1723014878
2024-08-07 13:49:00 Info: This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution - NoDerivatives 4.0 International License(see https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0/legalcode for more details).
2024-08-07 13:49:00 Info: © KubeOps GmbH, Hinter Stöck 17, 72406 Bisingen - Germany, 2023
2 - SSO with KOSI and Harbor
With KOSI-2.12.X we change some in the authentication process for the whole KubeOps brand. We are using now a SSO to interact with kubeops.net and our registry.
How to register an KubeOps account
Due to the Single-Sign-On (SSO) with KOSI 2.12.X, there are several ways to register an account. These are the two possibilities:
Register account via KubeOps.net
This is the usual way to register a user account. Scroll to the bottom of the page in the Download Area and click the SSO-Login button. You will be redirected to the SSO page where you can REGISTER a new user account.
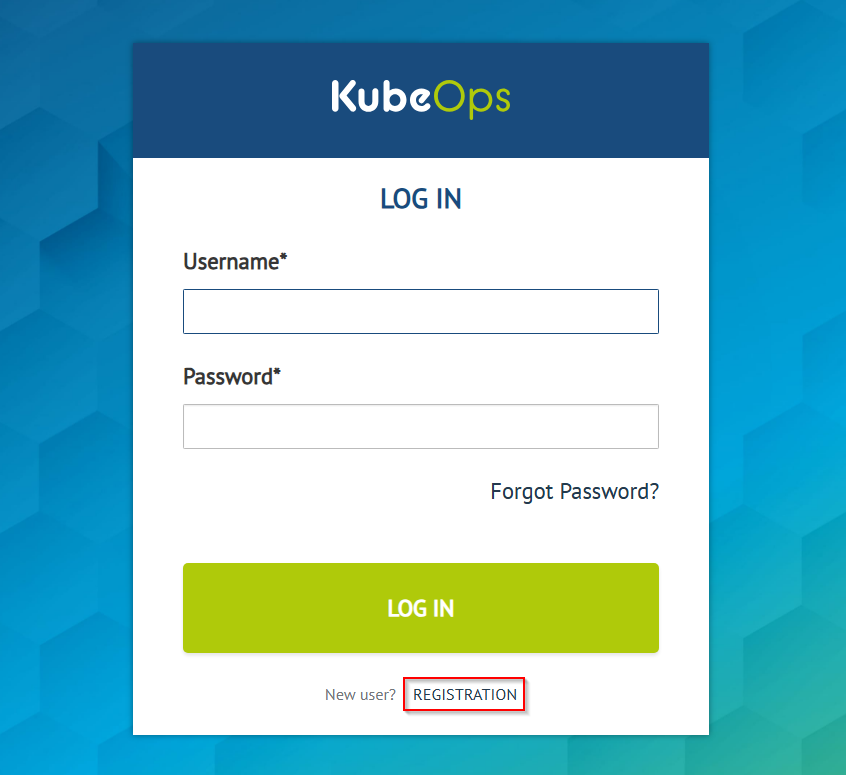
Register account via KubeOps-registry
Alternatively, you can register a user account by using the KubeOps-Registry page. Click on LOGIN WITH keycloak. You will be redirected to the SSO page where you can REGISTER a new user account.

How to use KOSI
After successful registration, you must log in once into the KubeOps-Registry. Once logged in, you can switch to KOSI 2.12.X and use it as normal.
How to manually push images in my KubeOps-Registry project space
To manually push container images into your KubeOps-Registry project space, you need to use your Harbor CLI secret for authentication when using podman.
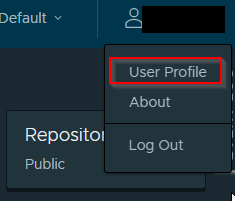
How to get your CLI secret
-
Click on your username and select User Profile.
-
On the User Profile page, you can copy or change your CLI secret if needed.
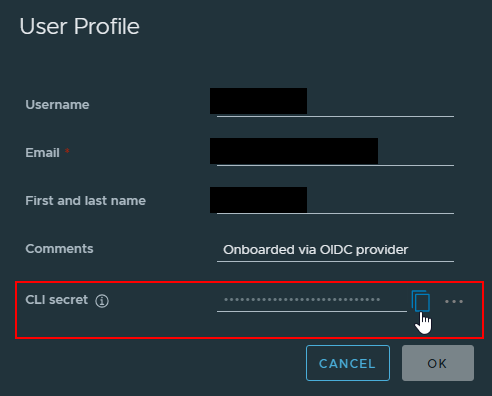
Now you can push your image using the CLI secret:
podman login registry.kubeops.net -u <username> -p <CLI_secret>
Note: Replace <username> with your KubeOps username and <CLI_secret> with your actual CLI secret.
3 - Install package from Hub
Installing KOSI packages from the KubeOps Hub simplifies the installation of packages and programs within a Kubernetes cluster. This guide outlines the steps for installing packages from public and private hubs, including offline installations.
Installing KOSI packages from KubeOps Hub
To install KOSI packages from the KubeOps Hub on your machines, follow these steps:
-
Search for the Package:
Use the kosi search command to find the desired package on the KubeOps Hub.
(Refer to kosi search for more info.)
-
Install the Package:
Copy the installation address of the desired package and use it with the kosi install command:
[root@localhost ~]# kosi install --hub <hubname> <installation address>
Note: The --hub parameter is used to install packages from the software Hub.
To be able to install a package from the software Hub, you must be logged in as a user.
Install from Private Hub
Example:
The package livedemo of user kosi with version 2.7.1 is to be installed from the private software Hub:
[root@localhost ~]# kosi install kosi/livedemo:2.7.1
Install from Public Hub
Example:
The package livedemo of user kosi with version 2.7.1 is to be installed from the public software Hub:
[root@localhost ~]# kosi install --hub public kosi/livedemo:2.7.1
Install along with yaml files
The -f parameter is used to provide YAML files from the user.
[root@localhost ~]# kosi install <package> -f <user.yaml>
Example:
The package livedemo of user kosi with version 2.7.1 is installed from the public software Hub with user-specific YAML files:
[root@localhost ~]# kosi install --hub public kosi/livedemo:2.7.1 -f userfile1.yaml
Install in specific namespace
The --namespace flag allows you to specify a Kubernetes namespace for the installation.
[root@localhost ~]# kosi install --hub <hubname> <package> --namespace <namespace>
Example:
The package livedemo of user kosi with version 2.7.1 is installed from the public software Hub in a custom Kubernetes namespace:
[root@localhost ~]# kosi install --hub public kosi/livedemo:2.7.1 --namespace MyNamespace
Note: If no --namespace parameter is specified, the default namespace will be used.
Install with specific deployment name
The --dname flag allows you to assign a specific name to the deployment.
[root@localhost ~]# kosi install --hub <hubname> <package> --dname <deploymentname>
Example:
The package livedemo of user kosi with version 2.7.1 is installed from the public software Hub with a deployment name set:
[root@localhost ~]# kosi install --hub public kosi/livedemo:2.7.1 --dname MyDeployment
If no --dname parameter is specified, a random deployment name will be generated.
Note: The deployment name is stored in the file /home/<user>/var/kubeops/kosi/deployment.yaml.
In these few steps, you can successfully install and use a KOSI package.
For additional functionality and features provided by KOSI, always refer to the Full Documentation.
Install on a machine with no internet connection
- Download the Package:
Use kosi pull on a machine with an internet connection to download the package:
[root@localhost ~]# kosi pull [package name from hub] -o [your preferred name] --hub public
-
Transfer the Package:
Move the downloaded package to the machine without an internet connection (which has KubeOps installed).
-
Install the Package:
Install the transferred package with the following command:
[root@localhost ~]# kosi install -p [package name]
4 - How to install and access the Plugins from the Hub
Installing and accessing plugins from the KubeOpsHub are straightforward steps to improve your KOSI experience. Below, you’ll find a guide on how to install and access the desired plugins.
How to access the Plugins
Note: Be sure you have a supported KOSI version 2.10.0 or higher.
All plugins are available as KOSI packages in the KubeOpsHub. Our plugins are grouped into several KOSI packages. To view the available packages, use the command:
KOSI Basic Plugins Version 1.6.X
kosi search --hub kosi-basic
2024-08-07 13:47:02 Info: KOSI version: 2.11.0.11_Beta0_1723014878
| User | Name | Version | Description | Install |
|------|---------------|-------------|--------------------|--------------------------------|
| kosi | basic-plugins | 1.5.0_beta0 | KOSI Basic Plugins | kosi/basic-plugins:1.5.0_beta0 |
| kosi | basic-plugins | 1.5.0 | KOSI Basic Plugins | kosi/basic-plugins:1.5.0 |
| kosi | basic-plugins | 1.4.0 | KOSI Basic Plugins | kosi/basic-plugins:1.4.0 |
| kosi | basic-plugins | 1.6.0_Beta0 | KOSI Basic Plugins | kosi/basic-plugins:1.6.0_Beta0 |
| kosi | basic-plugins | 1.4.2 | KOSI Basic Plugins | kosi/basic-plugins:1.4.2 |
| kosi | basic-plugins | 1.4.1 | KOSI Basic Plugins | kosi/basic-plugins:1.4.1 |
This package contains the following plugins:
| Plugin |
Version |
| template |
1.6.0 |
| helm |
1.6.0 |
| print |
1.6.0 |
KOSI Professional Plugins Version 1.6.X
kosi search --hub kosi-professional
2024-08-07 13:47:36 Info: KOSI version: 2.11.0.11_Beta0_1723014878
| User | Name | Version | Description | Install |
|------|----------------------|-------------|---------------------------|---------------------------------------|
| kosi | professional-plugins | 1.5.0_beta0 | KOSI Professional Plugins | kosi/professional-plugins:1.5.0_beta0 |
| kosi | professional-plugins | 1.4.0 | KOSI Professional Plugins | kosi/professional-plugins:1.4.0 |
| kosi | professional-plugins | 1.5.0 | KOSI Professional Plugins | kosi/professional-plugins:1.5.0 |
| kosi | professional-plugins | 1.4.2 | KOSI Professional Plugins | kosi/professional-plugins:1.4.2 |
| kosi | professional-plugins | 1.4.1 | KOSI Professional Plugins | kosi/professional-plugins:1.4.1 |
| kosi | professional-plugins | 1.6.0_Beta0 | KOSI Professional Plugins | kosi/professional-plugins:1.6.0_Beta0 |
This are the plugins which the packages contains:
| Plugin |
Version |
| template |
1.6.0 |
| helm |
1.6.0 |
| print |
1.6.0 |
| kubectl |
1.6.0 |
| bash |
1.6.0 |
| cmd |
1.6.0 |
| sh |
1.6.0 |
| editfile |
1.6.0 |
| fprint |
1.6.0 |
| if |
1.6.0 |
| loop |
1.6.0 |
| kosi |
2.11.0.10 |
| merge |
1.6.0 |
| exit |
1.6.0 |
| setfact |
1.6.0 |
KOSI Enterprise Plugins Version 1.6.X
kosi search --hub kosi-enterprise
2024-08-07 13:47:59 Info: KOSI version: 2.11.0.11_Beta0_1723014878
| User | Name | Version | Description | Install |
|------|--------------------|-------------|------------------------------|-------------------------------------|
| kosi | enterprise-plugins | 1.5.0 | KOSI Enterprise Plugins | kosi/enterprise-plugins:1.5.0 |
| kosi | piaoperator | 1.4.0 | Pia Operator Install Package | kosi/piaoperator:1.4.0 |
| kosi | enterprise-plugins | 1.4.2 | KOSI Enterprise Plugins | kosi/enterprise-plugins:1.4.2 |
| kosi | enterprise-plugins | 1.5.0_beta0 | KOSI Enterprise Plugins | kosi/enterprise-plugins:1.5.0_beta0 |
| kosi | enterprise-plugins | 1.4.0 | KOSI Enterprise Plugins | kosi/enterprise-plugins:1.4.0 |
| kosi | enterprise-plugins | 1.6.0_Beta0 | KOSI Enterprise Plugins | kosi/enterprise-plugins:1.6.0_Beta0 |
| kosi | enterprise-plugins | 1.4.1 | KOSI Enterprise Plugins | kosi/enterprise-plugins:1.4.1 |
This package contains the following plugins:
| Plugin |
Version |
| template |
1.6.0 |
| helm |
1.6.0 |
| print |
1.6.0 |
| kubectl |
1.6.0 |
| bash |
1.6.0 |
| cmd |
1.6.0 |
| sh |
1.6.0 |
| editfile |
1.6.0 |
| fprint |
1.6.0 |
| if |
1.6.0 |
| loop |
1.6.0 |
| kosi |
2.11.0.10 |
| merge |
1.6.0 |
| exit |
1.6.0 |
| setfact |
1.6.0 |
| auditlog |
1.6.0 |
| chmod |
1.6.0 |
| copy |
1.6.0 |
| firewall |
1.6.0 |
| firewallD |
1.6.0 |
| containerd |
1.6.0 |
| containerruntime |
1.6.0 |
| hostname |
1.6.0 |
| iptables |
1.6.0 |
| kubeadm |
1.6.0 |
| osCheck |
1.6.0 |
| packagemanager |
1.6.0 |
| pia |
1.6.0 |
| service |
1.6.0 |
| sudo |
1.6.0 |
How to install the Plugins
After installing the plugins with our KOSI install command, the plugins are automatically placed in the associated directory ($KUBEOPSROOT/plugins) and can be used directly.
kosi install --hub=<pluginhub> user/packagename:version
Example: The package enterprise-plugins of the user kosi with the version 1.6.0_Beta0 is to be installed from the kosi-enterprise hub.
kosi install --hub=kosi-enterprise kosi/enterprise-plugins:1.6.0_Beta0
Note: You can also use the Install Tab from the output to help with installation.
5 - How to build a KOSI package
Building a KOSI package is an easy and efficient way to build your own packages. This guide outlines the essential steps and commands to help you successfully build your KOSI package.
How to build your own KOSI package
This guide shows you how to create a KOSI package. KOSI can be downloaded only from our official website.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, check the following prerequisites:
- A machine with any of the following operating systems
- A text editor (Vi, VIM, Nano, etc.)
- An internet connection for downloading images or Helm charts
- All prerequisites for the KOSI installation
The package base
Using the kosi create command, all base components for building your package are generated.
Output:
2024-08-07 13:29:40 Info: KOSI version: 2.11.0.11_Beta0_1723014878
2024-08-07 13:29:41 Info: Write package.kosi to /root/demo
2024-08-07 13:29:41 Info: Write template.yaml to /root/demo
2024-08-07 13:29:41 Info: Write logo.png to /root/demo
2024-08-07 13:29:41 Info: Write docs.tgz to /root/demo
The package logic
The core of your package is defined in the package.kosi file. To build the package, you need additional files such as a Helm chart and a valuestemplate.yaml file. In this example, default values from the Bitnami WordPress Helm chart are used. A simple valuestemplate.yaml is required to build the package.
A valuestemplate.yaml
A Helm chart is required as well. Download the Bitnami WordPress Helm chart from ArtifactHub and prepare your values.yaml based on the default values. You can get both here.
A helm chart and values
helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
helm pull bitnami/wordpress --version 21.0.6
Note: This chart is not for production. It is only for demo purposes.
In the following example, the chart and the valuestemplate.yaml are added to the package.kosi. To convert the values, you need to call the template plugin, there you have to set the tmpl file and a target. Advanced templating makes it possible to split one large value file into smaller ones. In this case we use some of the default values but all values will be transfered.
To execute the helm install/upgrade operation, the helm plugin has to be called and for the target file is needed for the values.
You can also write update and remove operations for your package like in the example.
A clean is done in the remove section. With the helm plugin the helm deployment is removed and the cmd plugin call will remove the namespace.
A package.kosi example
languageversion = "1.0.0";
apiversion = "kubernative/kubeops/sina/user/v4";
name = "wordpressdemo";
description = "Deploys a wordpress helm chart";
version = "0.1.0";
docs = "docs.tgz";
logo = "logo.png";
files =
{
wordpressvaluestemplate = "valuestemplate.yaml";
chart = "wordpress-21.0.6.tgz";
}
install
{
template
(
tmpl = "valuestemplate.yaml";
target = "wordpressvalues.yaml";
);
helm
(
command = "upgrade";
tgz = "wordpress-21.0.6.tgz";
values = "['wordpressvalues.yaml']";
deploymentName = "wordpressdemo";
namespace = "wordpressdemo";
flags = "['--create-namespace ', '--install']";
);
}
update
{
template
(
tmpl = "valuestemplate.yaml";
target = "wordpressvalues.yaml";
);
helm
(
command = "upgrade";
tgz = "wordpress-21.0.6.tgz";
values = "['wordpressvalues.yaml']";
deploymentName = "wordpressdemo";
namespace = "wordpressdemo";
flags = "['--create-namespace ', '--install']";
);
}
delete
{
cmd(command = "echo delete worpressdemo helm deployment.");
helm
(
command = "delete";
deploymentName = "worpressdemo";
namespace = "wordpressdemo";
flags="['--wait']";
);
cmd(command="echo delete worpressdemo namespace.");
cmd(command="kubectl delete namespace worpressdemo");
}
Note: For more information about the package.kosi file, click here.
Build the package
When the package.kosi file is complete, build the package. During the build process, a package.tgz archive and a package.yaml file are created. To build your KOSI package, simply use the following command:
Note: The package.yaml file is generated only once. If a package.yaml already exists, KOSI will not generate a new one.
Install the package
To install your package, you need both the package.tgz and a values.yaml file containing the necessary configuration values. Typically, values are derived from the chart’s default values.
A values.yaml example
global:
storageClass: rook-cephfs
service:
type: NodePort
nodePorts:
http: 30123
mariadb:
enabled: true
auth:
rootPassword: topsecretChangeMe
password: secretChangeMe
primary:
persistence:
enabled: true
storageClass: rook-cephfs
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
persistence:
enabled: true
storageClass: rook-cephfs
To install the package, use the
kosi install command.
The
-p parameter is set for a local package.
The
-f parameter is set to hand over value files to the package.
kosi install -p package.tgz -f values.yaml
In this case, the output of the chart will describe your next steps:
kosi install -p package.tgz -f values1.yaml
2024-08-07 13:47:34 Info: KOSI version: 2.11.0.11_Beta0_1723014878
2024-08-07 13:47:35 Info: template write to /var/kubeops/kosi/e628d035-4700-4f55-a9ac-ab9217b8e79f/wordpressvalues.yaml
2024-08-07 13:47:35 Info: run cmd plugin
2024-08-07 13:47:35 Info: use plugin bash if available
2024-08-07 13:47:35 Info: Executing with non sudo privilegs
2024-08-07 13:47:36 Info: Release "wordpressdemo" does not exist. Installing it now.
NAME: wordpressdemo
LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Mar 26 10:47:35 2024
NAMESPACE: wordpressdemo
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
CHART NAME: wordpress
CHART VERSION: 21.0.6
APP VERSION: 6.4.3
** Please be patient while the chart is being deployed **
Your WordPress site can be accessed through the following DNS name from within your cluster:
wordpressdemo.wordpressdemo.svc.cluster.local (port 80)
To access your WordPress site from outside the cluster follow the steps below:
1. Get the WordPress URL by running these commands:
export NODE_PORT=$(kubectl get --namespace wordpressdemo -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}" services wordpressdemo)
export NODE_IP=$(kubectl get nodes --namespace wordpressdemo -o jsonpath="{.items[0].status.addresses[0].address}")
echo "WordPress URL: http://$NODE_IP:$NODE_PORT/"
echo "WordPress Admin URL: http://$NODE_IP:$NODE_PORT/admin"
2. Open a browser and access WordPress using the obtained URL.
3. Login with the following credentials below to see your blog:
echo Username: user
echo Password: $(kubectl get secret --namespace wordpressdemo wordpressdemo -o jsonpath="{.data.wordpress-password}" | base64 -d)
WARNING: There are "resources" sections in the chart not set. Using "resourcesPreset" is not recommended for production. For production installations, please set the following values according to your workload needs:
- resources
+info https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/
2024-08-07 13:47:36 Info: Helm upgrade successfully.
2024-08-07 13:47:36 Info: Installation successful
6 - How to update KOSI
Updating KOSI is a straightforward process that ensures you have the latest features and security enhancements. Follow this guide to update KOSI by downloading the appropriate RPM file and installing it on your system.
How to update KOSI
This guide shows you how to update KOSI. KOSI can be downloaded only from our official website.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, check the following prerequisites:
Before you begin, check the following prerequisites:
-
A machine with the RHEL 8 operating system.
-
You must have Helm installed on your machine.
Refer to the Helm Official Documentation for the Installation Guide.
-
For KOSI versions, you must have Podman installed on your machine.
Note: Before installing Podman, make sure that the number of user namespaces (max_user_namespaces) is specified on your system if you are a non-root user.
For more information, follow this GitHub link.
To install podman use command:
Important: KOSI supports only secure registries. If you use an insecure registry, it is important to list your registry as an insecure registry in the registry.conf file located at /etc/containers/registries.conf.
Update Steps
Every release of KOSI provides an RPM file for manual installation. You need to log in to your KubeOps account to download the RPM.
-
Create a KubeOps Account:
If you haven’t already, create a KubeOps account on the KubeOps website and log in to your account.
-
Download the RPM:
Download your desired version of the KOSI RPM file from our official download page:
https://kubeops.net/products/downloads/kosi-downloads-en
-
Update the KOSI RPM:
On your admin node, update KOSI by installing the new RPM, which will override the existing version. Run the following command:
sudo dnf install <path to rpm>/<kosi file name>
Note:
- Replace
<path_to_rpm> with the directory path where the file is located.
- Replace
<kosi_file_name> with the exact file name of the RPM (including the .rpm extension).
7 - How to install KOSI Proxy
The KOSI Proxy allows fetching packages and container images while blocking uploads to the internet and limiting access to a HUB. This guide details the installation and configuration steps for KOSI Proxy.
How to install KOSI Proxy
This guide shows you how to install the KOSI Proxy.
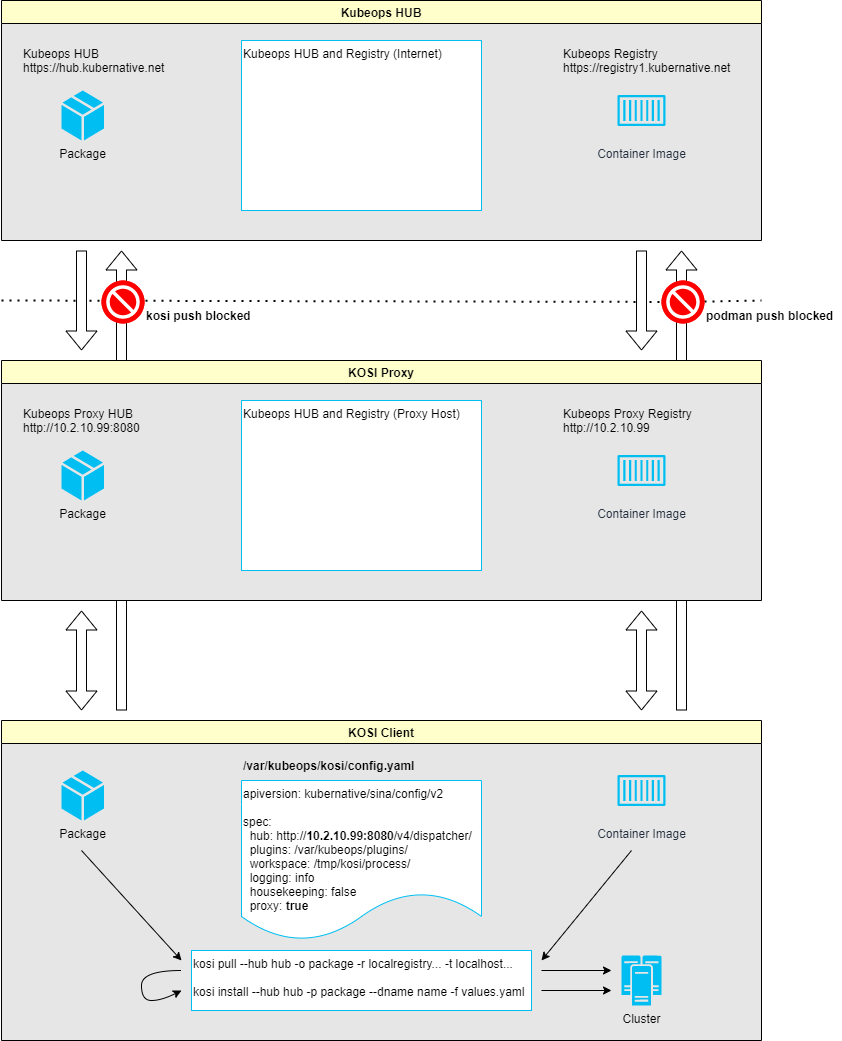
Architecture
The diagram shows the architecture of the KOSI Proxy.
Packages and container images can be fetched via the KOSI Proxy.
Uploading packages and container images to the internet is blocked.
Access can be limited to a HUB.
Prerequisites
To install the KOSI Proxy you need a dedicated VM with RHEL8 OS and root access.
Minimum requirements for the VM are:
- 4 CPU
- 8 GB RAM
- 50 GB Disk
The following software must be installed on this VM:
- docker
- docker compose
- kosi
# docker
subscription-manager register
subscription-manager refresh
subscription-manager attach --auto
dnf config-manager --add-repo=https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
dnf repolist -v
dnf install docker-ce
systemctl enable docker --now
systemctl status docker
# docker compose
curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/v2.24.5/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
# kosi
dnf install -y kosi*.rpm
#### Set KOSI config hub in __/var/kubeops/kosi/config.yaml__
```yaml
apiversion: kubernative/sina/config/v2
spec:
hub: https://hub.kubernative.net/v4/dispatcher/ # <- set hub
plugins: /var/kubeops/plugins/
workspace: /tmp/kosi/process/
logging: info
housekeeping: false
proxy: false # <- mandatory if kosi version >= 2.10.*
Install KOSI Proxy
If all prerequisites are met, the KOSI Proxy can be installed.
A values.yaml file is required for KOSI Proxy installation.
Below is an example values.yaml configuration for the environment:
# Proxy host IP address
proxyIP: 10.2.10.99
# Preprod config values
proxyPassthrough: preprod
proxyRegistry: registry.preprod.kubernative.net
aspnetcoreEnvironment: Development
# Prod config values
#proxyPassthrough: prod
#proxyRegistry: registry1.kubernative.net
#aspnetcoreEnvironment: Production
After the values.yaml file has been created, the KOSI Proxy can be installed via a kosi package.
The KOSI Proxy is installed in ~/kosi-proxy.
kosi install --hub public kubeops/kosi-proxy:2.10.0-alpha0 -f values.yaml
Start KOSI Proxy:
cd ~/kosi-proxy
docker-compose up -d
The KOSI Proxy is already configured during installation; however, additional parameters can be adjusted.
1. Hub Whitelist
The hub whitelist can be configured in the app settings file ~/kosi-proxy/data/download-v4/appsettings.json.
By default, the hubs kosi and kubeops are set.
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Microsoft": "Warning",
"System": "Warning",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information",
"Kubeops": "Debug"
},
"Console": {
"FormatterName": "simple",
"FormatterOptions": {
"SingleLine": false,
"TimestampFormat": "HH:mm:ss ",
"ColorBehavior": "Enabled",
"UseUtcTimestamp": false
}
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"Config": {
"RepositoryPath": "/service/repository",
"PermissionServiceUrl": "http://permission-v4/",
"ProxyPassthroughUrl": "https://hub.preprod.kubernative.net/v4/download/",
"GuestQuota": 1000000,
"HubWhitelist": "kosi, kubeops"
}
}
Install Harbor
Harbor is used as the registry endpoint in this setup.
1. Download installer
Download the Harbor offline installer:
# harbor
cd ~
curl -L https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/releases/download/v2.9.2/harbor-offline-installer-v2.9.2.tgz | tar -xvzf -
cd ~/harbor
cp harbor.yml.tmpl harbor.yml
Edit the harbor.yml
Change:
hostname: 10.2.10.99 # line 5
insecure: true # line 101
Comment out:
# port: 443 # line 15
# certificate: /your/certificate/path # line 17
# private_key: /your/private/key/path # line 18
3. Run install script:
1. Port Forward
To log in to Harbor, port 80 of the proxy host must be forwarded.
Example of port forwarding with ssh. Please adjust the values accordingly.
ssh -i "C:\Users\<user>\.ssh\id_rsa" -J <user>@10.9.112.19 -L 8080:10.2.10.99:80 root@10.2.10.99
You can then log in to Harbor -> http://localhost:8080
Default credentials:
- User: admin
- Initial Password: Harbor12345
2. Add Registry Endpoint
In Harbor, navigate to Administration → Registries → New Endpoint.
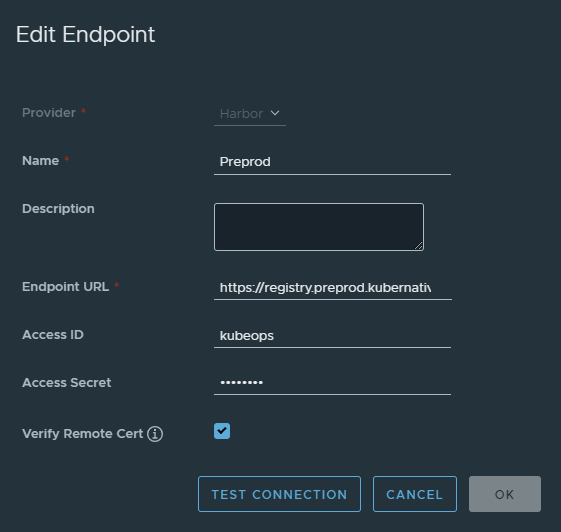
3. Add Project
In Harbor, navigate to Project → New Project.
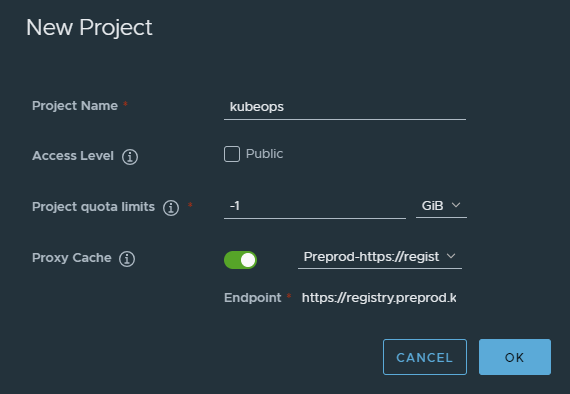
Manage applications with docker compose
1. KOSI Proxy
KOSI Proxy is installed in the folder ~/kosi-proxy.
cd ~/kosi-proxy
# show kosi proxy containers
docker compose ps
# show kosi proxy logs
docker compose logs -f
# stop kosi proxy
docker compose down
# start kosi proxy
docker compose up -d
2. Harbor
Harbor is installed in the folder ~/harbor.
cd ~/harbor
# show harbor containers
docker compose ps
# show harbor logs
docker compose logs -f
# stop harbor
docker compose down
# start harbor
docker compose up -d
8 - How to template within the package.kosi
How to template within the package.kosi"
TBA
9 - Create Kosi package
Creating a KOSI package is an easy and efficient way to create your own packages. This guide outlines the essential steps and commands to help you successfully create your KOSI package.
Creating Kosi package
kosi create
To create a Kosi package, you must first run the kosi create command in your directory.
The kosi create command creates four files (package.yaml, template.yaml, logo.png and docs.tgz) in the current directory. These files can be edited.
[root@localhost ~]# kosi create
Created files:
- package.yaml - Defines properties of the Kosi package. (see below)
- template.yaml - Required if the template engine Scriban is to be used.
- logo.png - A package-thumbnail with the size of 50x50px, for showing logo on the KubeOpsHub.
- docs.tgz - A zipped directory with the documentation of the package, for showing documentation on the KubeOpsHub.
The documentation of the package is written in markdown. The file for the documentation is called readme.md.
To edit the markdown, you can unzip the docs.tgz in your directory with the command tar -xzf docs.tgz and zip it again with the command tar -czf docs.tgz docs/ after you finished.
Note: Please name your markdown files inside docs.tgz without a version-tag (docs/documentation-1.0.0.md).
Do not change the file names of any of the files above generated with the kosi create command.
package.yaml
The package.yaml defines a package in a specific version as well as the tasks needed to install it. The tasks which are used in the package.yaml are plugins, which can be created by the user.
Elements:
includes.files: Describes the files which are inluded in the Kosi package.includes.containers: Used for docker images. A container for the docker images will be created when the kosi install, kosi update or kosi delete command is used.installation.tasks: The tree describes the tasks (Kosi plugins), which are executed with the kosi install command.update.tasks: The tree describes the tasks (Kosi plugins), which are executed with the kosi update command.delete.tasks: The tree describes the tasks (Kosi plugins), which are executed with the kosi delete command.
IMPORTANT: It is required to enter the package name in lowercase.
Do not use any docker tags (:v1.0.0) in your package name.
Example package.yaml
apiversion: kubernative/kubeops/sina/user/v4 # Required field
name: kosi-example-packagev3 # Required field
description: kosi-example-package # Required field
version: 0.1.0 # Required field
includes: # Required field: When "files" or "containers" are needed.
files: # Optional field: IF file is attached, e.g. "rpm, .extension"
input: "template.yaml"
containers: # Optional field: When "containers" are needed.
example:
registry: docker.io
image: nginx
tag: latest
docs: docs.tgz
logo: logo.png
installation: # Required field
includes: # Optional field: When "files" or "containers" are needed.
files: # Optional field:
- input # Reference to includes
containers: # Optional field:
- example # Reference to includes
tasks:
- cmd:
command: "touch ~/kosiExample1"
update: # Required field
includes: # Optional field: When "files" or "containers" are needed.
files: # Optional field:
- input # Reference to includes
containers: # Optional field:
- example # Reference to includes
tasks:
- cmd:
command: "touch ~/kosiExample2"
delete: # Required field
includes: # Optional field: When "files" or "containers" are needed.
files: # Optional field:
- input # Reference to includes
containers: # Optional field:
- example # Reference to includes
tasks:
- cmd:
command: "rm ~/kosiExample1"
- cmd:
command: "rm ~/kosiExample2"
kosi build
Now, after you created and edited the files from kosi create, you can simply build a Kosi package by just running the kosi build command in your directory.
[root@localhost ~]# kosi build
All files specified in the package.yaml are combined together with the package.yaml to form a kosi package.
In these few steps, you can successfully create and use the kosi package. This is the basic functionality offered by Kosi.
You can always explore Full Documentation to go through all the functionality and features provided by Kosi.





